Another installment of (in)secure Cloud storage

We know we sound like a broken record when we tell our clients “If you don’t own your server, you don’t own your data. Don’t put anything in the cloud you don’t want potentially exposed to the public.”, but time after time we show examples of why we keep repeating this mantra.
What Happened:
A major data leak by Securitas that affected several Latin American airports and other related companies was discovered by a cybersecurity firm called SafetyDetectives. In late January a team discovered that an Amazon S3 bucket had been left unsecured and exposed to public access, and contained over 1 million files relating to airport and security personnel.
Securitas, a large, well known multinational security company that has been in business for almost a century, has not made any public statements around the incident as of this posting. This isn’t the first time Securitas has had cybersecurity issues. In 2017 the Securitas CEO Alf Göransson had his personal identification stolen at the end of March, when someone applied for a loan in his name. The Stockholm District Court then declared Göransson bankrupt without informing the CEO prior to its decision.
The Breach (From SafetyDetectives briefing):
Securitas left its Amazon S3 bucket open and accessible, without any authentication procedures in place. The misconfigured bucket has therefore exposed almost 1.5 million files, equating to about 3TB of data.
The bucket’s exposed information included employee Personally Identifying Information and sensitive company data of at least four airports in Colombia and Peru: El Dorado International Airport (Bogota D.C, COL), Alfonso Bonilla Aragón International Airport (Valle del Cauca, COL), José María Córdova International Airport (Antioquia, COL), and Aeropuerto Internacional Jorge Chávez (Lima, PE). As mentioned, unobserved files may have exposed other airports and places throughout Colombia, the rest of Latin America, or even the rest of the world.
They observed two main datasets containing the information of Securitas employees and airport employees: photos of ID cards and other unmarked photos.
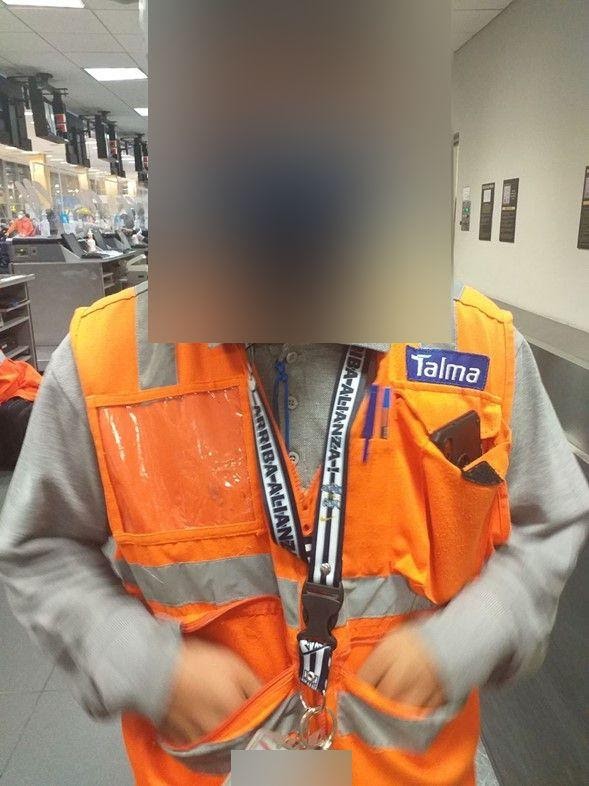
Photos of ID cards featured on the bucket. There were an estimated 1 million files of this type on the Securitas misconfigured bucket. These files revealed the personal information of employees at the four aforementioned airports that are using Securitas’ services.
Photos of ID cards reveal several forms of employee Personally Identifying Information, including:
- Full names, incl. first names and surnames
- Photos of employees
- Occupations
- National ID Number

Other unmarked photos featured among the bucket’s content too. There were about 300,000 files of this type. These photos leaked the data of airports, airport employees, and associated companies.
Specifically, these files exposed employees’ personal data, sensitive client data (airports), and the sensitive data of associated companies, such as airlines. Exposed data includes:
- Photos of employees
- Photos of planes
- Photos of fueling lines
- Photos of luggage being loaded/unloaded

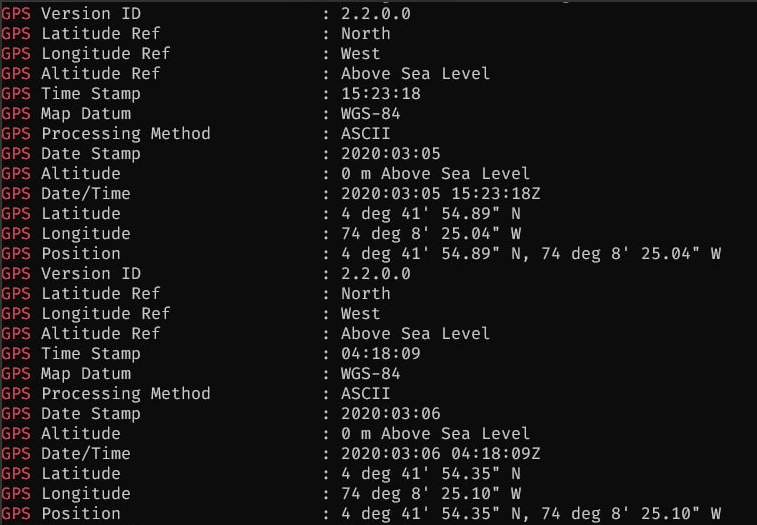
In addition to the information mentioned above, the two primary datasets analyzed on the bucket (photos of ID cards and other unmarked photos) contained Exchangeable Image File Format (EXIF) data that exposed specific information related to each photo. Exposed EXIF data includes:
- Device models (of the cameras used)
- GPS locations of photos, incl. coordinates and GPS maps
- Time & date of photos
What it Means to Us
It may be some time before there is any assessment of the extent of damage the data breach, but this obviously serves as an example of how careless data management can cause serious security implications for your firm or those of your clients. In evaluating software application strategies for our clients, we always ask these simple questions:
- What is the criticality if this information if it is leaked to the public?
- Can the solution be self-hosted on the Client’s own private network?
- Does it really NEED to be a cloud application?
- If so, how can we mitigate the potential damage if there is a breach?
Additional measures like a Type I or Type II SOC report are helpful, but likely wouldn’t have prevented the Securitas data breach discussed above. Regular and ongoing security audits, along with well defined and enforced data management and security policies and procedures are the only real defense against these kinds of mishaps.
This won’t be the last time we see this either, as the Cloud becomes more and more integrated into corporate IT strategies, it will happen again, and again, and again.
